42 plastids diagram with labels
Plastids- Definition, Structure, Types, Functions and Diagram Plastid is a double membrane-bound organelle involved in the synthesis and storage of food, commonly found within the cells of photosynthetic plants. Plastids were discovered and named by Ernst Haeckel, but A. F. W. Schimper was the first to provide a clear definition. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › History_of_botanyHistory of botany - Wikipedia Diagram showing the sexual parts of a mature flower It was Rudolf Camerarius (1665–1721) who was the first to establish plant sexuality conclusively by experiment.
Plant and Animal Cell: Labeled Diagram, Structure, Function - Embibe Plastids: 1. Double membrane-bound structures found only in the plant cells. 2. This is an autonomous organelle. 3. There are stroma or matrix and grana or stacked discs that are involved in photosynthesis. 4. Grana are the site for photochemical reactions of photosynthesis, while stroma is the site for biochemical reactions of photosynthesis. 5.

Plastids diagram with labels
Study Notes on Genetics of Plastids (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion The below mentioned article provides a study note on Genetics of Plastids. In the cytoplasm of the plant cells are found many small cytoplasmic bodies, called plastids. These plastids are of several types, such as, chloroplast, leucoplast, chromoplast and so on. Plastids arise from smaller particles, the proplastids, found in the egg cytoplasm. Plastids In Plant Cell Diagram Structure : Functions and Diagram - ACTUINDE Plastids- Definition, Structure, Types, Functions and Diagram They were discovered and named by Ernst Haeckel, while A. Mayer and Schimper first used the term plastid. Most cultured cells that are relatively large compared to other plant cells have very long and abundant stromules that extend to the cell periphery. Plant Cell-Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram Figure: Labeled diagram of a plant cell, created with biorender.com The plant cell is comprised of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin, as well as plastids, which are essential for photosynthesis and starch storage, and enormous vacuoles that control cell turgor pressure.
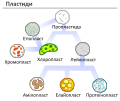
Plastids diagram with labels. Plastids: Definition, Diagram, Types, and Plastid Function - Embibe Types of Plastids and Functions of Plastids Plastids are further divided into 3 types that have different functions and some have biological pigments as well. 1. Leucoplasts 2. Chromoplasts 3. Chloroplasts Leucoplasts These colourless Plastids possess internal lamellae and do not contain photosynthetic and grana pigments. EOF Labeled Plant Cell With Diagrams | Science Trends The parts of a plant cell include the cell wall, the cell membrane, the cytoskeleton or cytoplasm, the nucleus, the Golgi body, the mitochondria, the peroxisome's, the vacuoles, ribosomes, and the endoplasmic reticulum. Parts Of A Plant Cell The Cell Wall Let's start from the outside and work our way inwards. Chloroplast- Diagram, Structure and Function Of Chloroplast - BYJUS These plastids are double-membraned cell organelles which play a primary role in the manufacturing and storing of food. ... The chloroplast diagram below represents the chloroplast structure mentioning the different parts of the chloroplast. The parts of a chloroplast such as the inner membrane, outer membrane, intermembrane space, thylakoid ...
Cell Organelles- Definition, Structure, Functions, Diagram However, some organelles are specific to one particular type of cell-like plastids and cell walls in plant cells. Image created using biorender.com. List of Cell Organelles. Cell membrane (Plasma membrane/ Plasmalemma) ... Labeled Diagram; Animal Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram; Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes ... Plant Cell Diagram Plastids Structure : Functions and Diagram - ACTUINDE Friday, February 12th 2021. | Diagram Plant Cell Diagram Plastids. Plastids are the site of manufacture and storage of important chemical compounds used by the cells of autotrophic eukaryotes. It is the second largest organelle of the cell which is bounded by a double unit membrane and may be colored or colorless. Plastids: Types, Structure and Function (With Diagram) Plastids may be coloured or colourless and are of three types. The leucoplasts are the colourless plastids principally serving the purpose of storage. On the basis of nature of storage compound, leucoplastids are amyloplasts (starch), elaioplasts (oil) or aleuroplasts (protein). The green plastids or chloroplastids are needed for photosynthesis. Animal Cells: Labelled Diagram, Definitions, and Structure - Research Tweet Animal Cells Organelles and Functions. A double layer that supports and protects the cell. Allows materials in and out. The control center of the cell. Nucleus contains majority of cell's the DNA. Popularly known as the "Powerhouse". Breaks down food to produce energy in the form of ATP.
doku.pub › documents › nelson-biology-12pdf-30j71j2z320wNelson Biology 12.pdf [30j71j2z320w] - doku.pub (a) Define osmosis and diffusion. (b) Make a sketch to represent each process in (a). Label your sketch. (c) Explain why these processes are essential for cellular function. K/U C 15. Draw a diagram to explain what happens to a cell in each of the following types of solutions. K/U C (a) isotonic (b) hypotonic (c) hypertonic Skills Review 16. Plastids: Definition, Structure, Types, Functions and Diagram Plastids are double-membrane organelles that contain pigments that are helpful in the process of Photosynthesis and govern the change in the colours of the cells. Plastids also act as storage devices for starch and help in the synthesis of various molecules like fatty acids and terpene. They are found in plants and algae and are responsible for ... Plastids: Everything You Need to Know and More Plastids are a diverse group of double-membrane bound organelles found in most plants and algae. They may also be found in ferns, moss, parasitic worms and marine mollusks. Apart from photosynthesis, these organelles also assist in food storage and synthesis of compounds such as lipids, amino acids and carbohydrates. Plastid - Wikipedia There is an illustration of stages depicted by the diagram mentioned above in which it is shown inter-conversion of Plastids In 1977 J.M Whatley proposed a plastid development cycle which said that plastid development is not always unidirectional but is a cyclic process several times.
Chloroplast Structure and Function in detail with Labelled Diagram The chloroplasts are the cell organelles which consist of these pigments. The 3 types of pigments present in plants are chlorophyll, carotenoids, and anthocyanins. Chlorophyll imparts the green color to plants. Plastids are membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelles that can be found in the cells of plants and algae.
Plant Cell-Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram Figure: Labeled diagram of a plant cell, created with biorender.com The plant cell is comprised of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin, as well as plastids, which are essential for photosynthesis and starch storage, and enormous vacuoles that control cell turgor pressure.
Plastids In Plant Cell Diagram Structure : Functions and Diagram - ACTUINDE Plastids- Definition, Structure, Types, Functions and Diagram They were discovered and named by Ernst Haeckel, while A. Mayer and Schimper first used the term plastid. Most cultured cells that are relatively large compared to other plant cells have very long and abundant stromules that extend to the cell periphery.
Study Notes on Genetics of Plastids (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion The below mentioned article provides a study note on Genetics of Plastids. In the cytoplasm of the plant cells are found many small cytoplasmic bodies, called plastids. These plastids are of several types, such as, chloroplast, leucoplast, chromoplast and so on. Plastids arise from smaller particles, the proplastids, found in the egg cytoplasm.











Post a Comment for "42 plastids diagram with labels"